The European Commission has launched the draft Delegated Regulation (EU) 2024/1701, amending Regulation (EC) No 1234/2008 with regard to modifications of marketing authorisations (MAs) for human medicines (Regulation on variations) within the existing legal framework of Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 and Directive 2001/83/EC.
Transition period and objectives of the new regulation
Although the first draft of the delegated regulation entered into force on 1 January 2025, with the main goal of achieving a simpler, clearer, and more flexible legal framework while ensuring the same level of public health protection, we are currently in a transition period, awaiting full implementation starting 15 January 2026, when official national publications of a second draft will include clarifications and new concepts regarding the current regulation.
These updates to the so-called “variation guideline” for human medicines aim, among other things, to reduce administrative burden for both authorities and Marketing Authorisation Holders (MAHs).
In short, this represents another step in the legislative reform to create greater harmonisation across Member States and optimise resources.

Delegated Regulation 2024/1701, proposes changes in the classification of variations and changes on the application of the procedures established in different chapters of the same. Most of the changes in the classification are mainly due to the new requirements introduced by the EU Pharmacovigilance legislation and other changes in Quality.
In the introductory framework, the alternatives of extensions to marketing authorizations (Line Extensions) are maintained, together with the priority focus on public health protection through updates of influenza and coronavirus vaccines (Annual Updates). In addition, the importance of implementing urgent regulatory measures (Urgent Safety Restrictions, URS) in the event of risk situations is emphasized, ensuring health safety.
What changes are observed over time?
As of January 1, 2025, the Authorities published the first changes regarding variation regulations, aimed at facilitating administrative procedures both for the pharmaceutical companies and for the European agencies that must evaluate them, starting with a clear objective: human medicinal products. In this context, a new version of the eAF (electronic application form) was also introduced to implement all these proposed changes.
Although the same classification of variations remains in place as before (minor variations type IA, IB, and major variations type II, line extensions, and urgent safety restrictions), in 2025, for the first time, new terms for minor type IA variations appeared, such as Super Grouping and Annual Report, and the concept of worksharing for type IB and type II variations was emphasized.
Currently, a new draft is available, which is under translation and will be implemented starting January 15, 2026. This draft not only maintains all the proposed changes during the transition period in force since January 1, 2025, but also includes clarifications regarding procedures and administrative management, along with some relevant changes in the Annexes.
New clarifications appear in the introduction, such as the incorporation of new definitions that were not present in previous versions. The concepts of “Relevant Authority” (competent authority of each concerned member state or the agency in the case of centralized procedures) and “Reference Authority” (in the context of supergroupings and worksharing, the agency selected to act as the reference for the evaluation of the proposed modification) are introduced to designate the different authorities involved in the management and evaluation process.
In the context of managing variations to be submitted (whether IA, IB, or II), the term “Grouping” is defined, which was not incorporated in Regulation (EC) No 1234/2008 as a concept, although it was used according to European guidelines.
Additionally, regarding minor IA variations, the new term introduced in 2025, “Supergrouping”, is maintained for this type of variation.
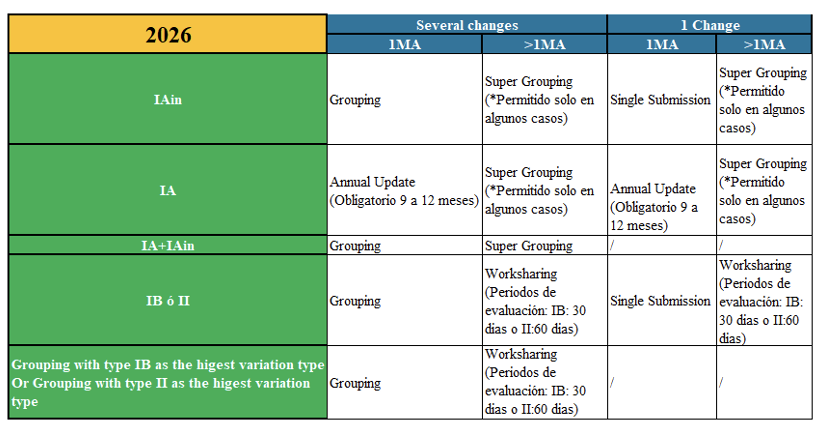
Supergrouping
Supergrouping (a group of IA/IA-IN modifications that may be submitted in a single notification for several Marketing Authorizations (MAs) owned by the same holder, provided that the notified modifications are identical for all the MAs concerned) requires prior confirmation by the authorities for submission, since the assignment of the variation number is necessary. It is possible in the following cases:
-
One or several minor type IA modifications, notified at the same time for several marketing authorizations granted under the mutual recognition, decentralized, or purely national procedure in several Member States.
-
One or several type IA modifications, notified at the same time for several marketing authorizations granted under the mutual recognition or decentralized procedure where the same reference Member State applies to those procedures.
-
One or several minor type IA modifications, notified at the same time for several marketing authorizations granted under the centralized procedure.
Continuing with changes in minor type IA variations, in 2025 the term “Annual Reporting” also appears, which makes it possible for IA variations (whether IA, IA-IN, and/or a combination of both) to be compiled and submitted as an Annual Update, provided they comply with the conditions of the guideline. The IA variations included in this grouping do not need to be related to each other. They must be submitted within twelve months (between 9 and 12) after the implementation of the first modification. This type of notification does not allow for a mixture of procedures: either all national or all European, but not both.
Reinforcement of worksharing
In addition, the concept of worksharing is reinforced for minor type IB variations as well as for major type II variations, when they affect several marketing authorizations (of the same holder). The evaluation period for the major modification will be the standard one (IB: 30 days or II: 60 days). In previous versions, its use was optional for the holder; now its use is emphasized.
Considering the emerging medical device legislation and its interrelation with pharmaceutical products, the variations guideline also includes relevant changes in this respect. Therefore, when a medicinal product requires the use of a medical device for its administration, the new medical device regulation and the new quality documentation guidelines for medicines will be taken into account, measuring the impact/risk on the administration, quality, safety, and/or efficacy of the medicinal product.
We cannot forget that combination products (composed of two or more regulated components, i.e., drug/device, biological/device, drug/biological, or drug/device/biological product, which are combined or mixed physically, chemically, or in any other way and produced as a single entity) must be strictly regulated and controlled both for the medical device and for the drug component.
Restructuring of the Annexes
Ultimately, the current variations guideline implies a restructuring with a simpler vision of the categorization of variations.
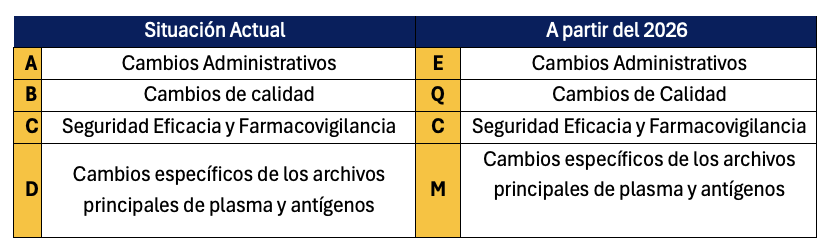
However, within this “Draft” of 2026, the major change affecting the Annexes is the change in the classification that had remained since 2024. Instead of the four chapters of the Annexes classified as A, B, C, D, starting in 2026 they will be classified as E, Q, C, M.
The Delegated Regulation 2024/1701 provides the pharmaceutical industry with further progress in terms of clarity, more defined timelines, and tools such as Supergrouping and Annual Update, which are essential to reducing administrative procedures and facilitating optimized management for Marketing Authorization Holders (MAHs), while reinforcing transparency across all processes.


